Metal wire or carbon is the material used for their construction and over a wide range of environmental conditions, they maintain a stable resistance value. They produce heat, unlike lamps which produce light as they dissipate electric power in an electric circuit that is working. However, the sole purpose of using the resistors is to provide a precise quantity of electrical resistance instead of producing usable heat. A zig-zag line is the most common symbol used to represent the resistor and the value of resistance is measured in Ohm which is the unit named after German physicist George Simon Ohm in the 19th century. And the resistor symbol can be drawn in a zig-zag shape either vertically or horizontally. But the other hand the resistors look like small tubes or cylinders equipped with two wires available for connecting them to a circuit in real life. Rather than a fixed resistance the resistors can also be shown to have a varying resistance. This phenomenon occurs when the resistor is designed in a way in the form of a physical device that provides an adjustable resistance or a component having unstable resistance.
A component will have a variable resistance when it's drawn in the form of a diagonal arrow through a zig-zag line. The symbols for a fixed and a variable resistor are given below in the diagram.

Resistor in Series and Parallel:
As we have described the term resistance above and explained the basic design of resistors, we will discuss the series and parallel combinations of the resistors and their properties. As we know the resistor being an ohmic device is used to limit the flow of current where V=IR. When more than one circuits are attached to a battery in a circuit the equivalent resistance of the circuit controls the amount of current in the circuit. The individual value of the resistor and combination define the value of the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Series and parallel are the two simplest combinations of the resistors. In the case of a series combination, the current through each resistor is the same because the output current of the first resistor becomes the input for the second resistor connected next to the first resistor. On the other hand in the case of the parallel resistor, one of the terminals of each resistor is connected and all the terminals of the other side are also connected or in other words, are connected to a common point. Due to the potential drop on each of the resistors, every resistor has an individual value of the current that could be different from other resistors depending on the resistor. The equivalent current flow in the circuit is equivalent to the sum of current flowing through each parallel connection.
(a) Resistors in the Series Combination:
When the current through the resistors flows sequentially the resistors are said to be in the series as shown in the diagram below. Suppose we have four resistors connected in series and voltage V is applied to them, the algebraic sum of the individual resistances will be the equivalent resistance of the circuit.

Because the current flowing through each resistor is the same when voltage V is applied to them. The resistance value of the resistors and the applied voltage to the circuit define the total current flowing through the circuit. Potential drop occurs at each resistor and we can find the potential drop on each resistor with the help of ohms law V = IR. So the total resistance will be

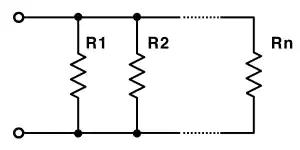
(b) Resistors in the Parallel Combination:
The diagram below illustrates the parallel connection of the four resistors if we apply the voltage V on the circuit the potential drop on each resistor will be the same and by using Ohms law equation I=V/R the amount of current can be found where the voltage will be constant for each resistor.

So in the case of the parallel circuit, the total reciprocal value of the resistor of the circuit will be equal to the reciprocal value of each resistor as given by the equation below.

Application of Resistors:
Controlling the flow of current is the main purpose of the resistor. The flow of electricity is slowed down by the collision of the electrons with the ions which produce the heat and lower the current. Less current for a given voltage flow in the resistor if a resistor is said to have high resistance. In our daily life resistors are used in DMMs, oscillators and telecommunication, transmitters, etc. Some important applications of resistors are given below.
· As discussed above changing the value of resistance affects the flow of current inside a circuit. This phenomenon is used to control the loudness of the amplifier, speed of the motor, or pitch of musical tone by controlling the amount of current flowing through these electrical systems with the help of resistors so resistors play a vital role in the in-circuit functions.
· When the electrical components are required to work at a lesser voltage than the applied voltage dividing is done on the circuit by connecting the series resistors. This addition of a series resistor will help to drop the voltage equally across each resistor.
· In heaters, microwaves, toasters, and electric stoves the heat-generating nature of resistors is used. Due to very high temperature the metal filament of the light bulb glows white-hot when electricity is passed through it.
· As the LEDs are very sensitive to the electric current too much current passed inside an LED or transistor can be dangerous. For the LEDs and other smaller electrical components to work at a desired current range the use of a resistor in a circuit will help.